The way we watch television is changing dramatically. Gone are the days when viewers had to arrange their schedules around broadcast times or pay for hundreds of channels they never watch. Internet Protocol Television (IPTV) is at the forefront of this transformation, offering a flexible, personalized viewing experience that puts control back in the hands of consumers.
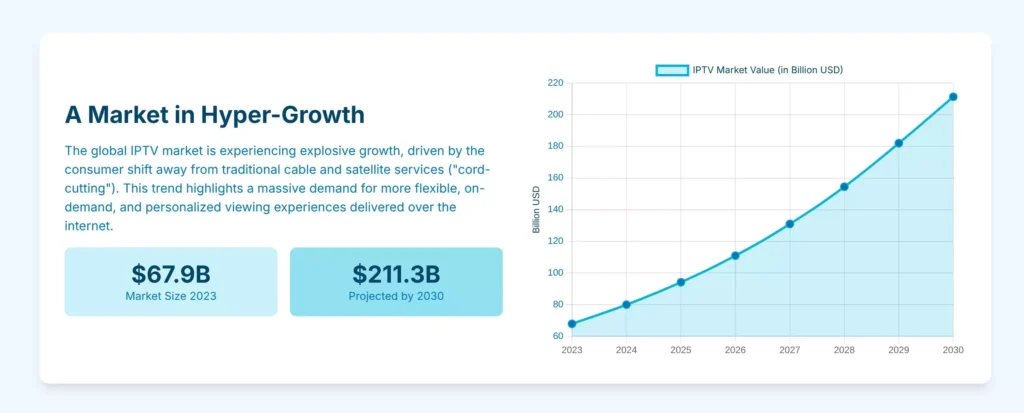
As of 2025, IPTV has roughly 250 million subscribers globally and the industry is valued at approximately $187 billion, marking a significant jump from $160 billion in 2024. This explosive growth reflects a broad shift from traditional TV to internet-based streaming, with analysts dubbing IPTV “the television of the future.”
But what exactly is IPTV, and why is it reshaping the entertainment landscape? This comprehensive guide will demystify IPTV technology, explain how it works, and help you understand whether it might be the right choice for your viewing needs.
What is IPTV? Definition and Basics
internet Protocol Television (IPTV) is essentially TV delivered over the internet using IP networks, rather than through traditional terrestrial, cable, or satellite signals. Think of it as television content streamed directly to your devices through your internet connection.
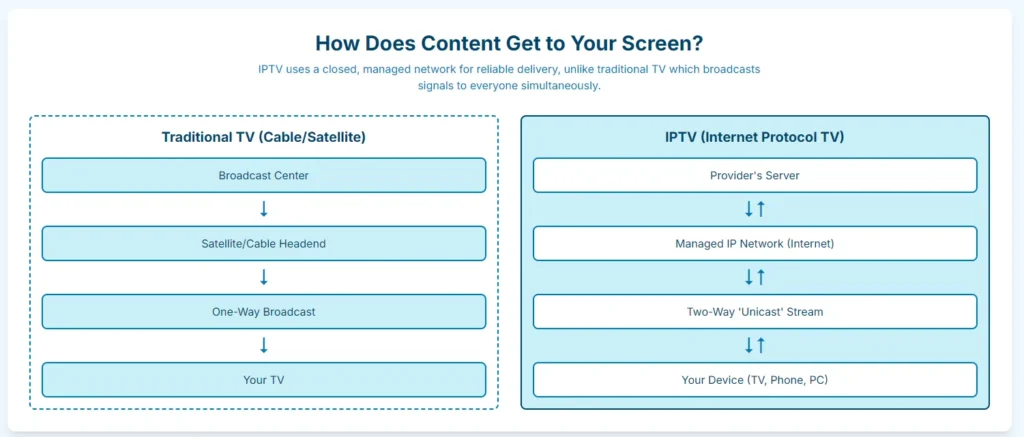
The key distinction lies in how content reaches you. Traditional broadcast and cable TV send out all channels simultaneously over the air or via coaxial cables. You simply “tune in” to whatever channel you want from this constant stream of programming. IPTV operates differently – it sends content on demand through data packets over networks, delivering only what you actually choose to watch.
This technology is often offered by telecom or broadband providers as part of their service bundles. For example, services like Verizon Fios TV, AT&T U-verse, or BT TV in the UK are classic examples of IPTV delivered by telecommunications companies over their managed networks.
What makes IPTV particularly appealing is that it combines the comprehensive channel lineups of traditional TV with the flexibility and interactivity of internet-based services. You get live television when you want it, plus advanced features that simply aren’t possible with conventional broadcast methods.
How Does IPTV Work? Technical Overview
Understanding IPTV’s technical foundation helps explain why it offers such superior flexibility compared to traditional TV.
The Basic Process
When you select a channel or video on an IPTV service, that content is encoded into IP packets and delivered over the internet to your device. The IPTV system typically uses either a private, managed network (for telecom IPTV services) or the open internet (for streaming services) to send this data.
Unicast vs. Broadcast: A Fundamental Difference
Traditional television uses a broadcast model – one signal sent to many viewers simultaneously. Every channel is constantly transmitted whether anyone is watching or not. IPTV primarily uses a unicast approach, where a unique stream is sent to each viewer based on what they choose to watch. This means only the requested program streams to you, making the system incredibly efficient and enabling true on-demand viewing.
For live television, IPTV can use IP multicast protocols, where a single stream can be accessed by multiple viewers watching the same live channel. But for Video on Demand content, each viewer gets their own dedicated unicast stream.
Equipment and Access
Most IPTV services require either a set-top box (STB) or a compatible app to receive and decode the streams. The set-top box, often provided by the IPTV service, connects to your internet and then to your TV, converting the IP signals into video output your television can display.
Increasingly, dedicated apps on smart TVs, phones, tablets, or streaming devices like Roku and Amazon Fire Stick can serve this role, sometimes eliminating the need for separate hardware from the provider.
Quality of Service Advantages
Many IPTV systems, especially those from Internet Service Providers, operate on managed networks that can guarantee quality of service (QoS). This means they can prioritize TV traffic on their network, ensuring smooth playback without buffering – a significant advantage over pure internet streaming that competes with all other internet traffic.
However, IPTV performance still heavily depends on having a high-speed internet connection, particularly for HD or 4K content.
Types of IPTV Services
IPTV’s versatility shines through its diverse service offerings, each designed to address different viewing preferences and needs.
Live Television
IPTV can stream live TV channels in real-time, just like cable or broadcast television. You can watch live news, sports, or any scheduled programming as it happens. This works through IP multicasting for efficiency, allowing thousands of viewers to watch the same live event without overwhelming the network infrastructure.
Time-Shifted TV
One of IPTV’s most popular features is its time-shifting capabilities:
- Catch-up TV allows viewers to watch recent broadcasts on demand. If you missed a show that aired yesterday, you can simply select it from the service’s archive and stream it whenever convenient.
- Start-over TV lets you restart a live program from the beginning, even if it’s already in progress.
- Pause and rewind live TV functionality means you can pause a live broadcast to answer the phone or rewind to catch something you missed.
Video on Demand (VOD)
VOD libraries are perhaps IPTV’s biggest draw. These vast digital catalogs of movies, series, and shows can be selected and streamed instantly. Unlike Netflix or similar services that you access separately, IPTV VOD is typically integrated into your main TV service, providing thousands of titles accessible through the same interface you use for live TV.
Interactive Services
IPTV isn’t just passive viewing – it can include interactive applications like:
- On-screen caller ID during TV watching
- Voting in live shows
- Interactive advertisements
- Multiple camera angle selection during sports events
- Integration with social media and other apps
These features are possible because IPTV uses two-way communication between your device and the provider’s servers.
IPTV vs. Traditional TV vs. OTT Streaming
Understanding how IPTV compares to other television delivery methods helps clarify its unique position in the entertainment landscape.
IPTV vs. Cable/Satellite TV
| Feature | Traditional TV | IPTV |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission | Coaxial cable networks or satellite signals | Internet (broadband/fiber) |
| Content Delivery | Linear broadcast (all channels transmitted constantly) | On-demand delivery (only requested content streams) |
| Interactivity | Mostly one-way communication | Two-way communication enabling pause, rewind, VOD |
| Geographic Flexibility | Tied to physical infrastructure at your home | Can work anywhere with sufficient internet connection |
| Equipment | Cable box or satellite receiver | Set-top box or app-based access |
| Customization | Large, inflexible bundles | More flexible packages and à la carte options |
IPTV’s internet-based delivery means it’s not geographically locked to infrastructure the same way cable is. You could potentially use your IPTV account anywhere with a good internet connection (subject to provider policies and licensing restrictions).
IPTV vs. OTT (Over-The-Top) Streaming
While both use the internet, there’s an important distinction:
- IPTV usually refers to services that mirror traditional TV structure (live channels, comprehensive packages) delivered by ISPs or specific providers, often requiring a subscription to that particular service.
- OTT services like Netflix, Hulu, or YouTube TV are delivered “over the top” of the open internet by third-party companies not tied to your internet provider.
The lines are increasingly blurring, with services like YouTube TV and Hulu + Live TV functioning as “OTT IPTV” – providing live channels via the internet but accessible to anyone with an internet connection.
From a consumer perspective, both arrive through your internet connection. The main practical difference is who provides it and how comprehensive the service is. If your telecom company offers a TV package over their network, that’s classic IPTV. If it’s an independent app like Netflix, that’s OTT streaming.
Advantages of IPTV for Consumers
IPTV offers several compelling benefits that explain its rapid global adoption.
On-Demand Flexibility
The primary benefit is content when you want it. No more scheduling your life around TV guides or missing your favorite shows. IPTV’s VOD libraries and time-shifting features mean you watch on your own schedule, fundamentally changing the relationship between viewers and television programming.
Greater Choice and Personalization
IPTV often allows users to choose their channel packages or subscribe to specific content bundles, rather than being forced into large cable packages filled with unwanted channels. Recommendation engines and user profiles help personalize the viewing experience, suggesting shows and creating watchlists based on your preferences.
Multi-Device Viewing
Unlike traditional cable that’s confined to specific TV sets, IPTV typically works across multiple devices. Watch on your main TV at home, then continue the same show on your tablet during your commute, or on your phone during lunch break. This mobility represents a fundamental shift from location-bound television consumption.
Interactive Features
IPTV’s two-way communication enables features impossible with traditional broadcast:
- Pause and rewind live TV when life interrupts
- Start-over functionality if you miss the beginning of a program
- Rich on-screen menus with detailed program information
- Integration with other services and apps
- Multiple viewing options for sports events
High-Quality Content
With adequate bandwidth, IPTV can deliver high-definition and 4K Ultra HD content, often with superior picture quality compared to compressed cable signals. The IP-based delivery isn’t limited by broadcast spectrum constraints, allowing for less compression and better visual fidelity.
Cost Savings Potential
Many consumers find IPTV solutions more affordable than traditional cable packages. IPTV in the US can cost a fraction of cable TV’s monthly price, and the ability to choose only wanted channels or mix-and-match services helps optimize spending. When bundled with internet service, IPTV can provide additional savings through “triple play” packages.
Challenges and Considerations
While IPTV offers numerous advantages, it’s important to understand its limitations and requirements.
Internet Dependency
IPTV’s biggest consideration is its absolute reliance on a reliable, high-bandwidth internet connection. If your internet is slow or goes down, so does your TV service. Unlike cable, which can work independently of your internet connection, IPTV is only as good as your network connectivity.
During peak usage times or on congested networks, IPTV quality might suffer from buffering or reduced resolution if Quality of Service isn’t properly managed.
Bandwidth and Data Usage
Streaming hours of IPTV content consumes significant data. HD streaming typically uses 3-5 GB per hour, while 4K can consume 15-25 GB hourly. Families watching IPTV regularly could easily use hundreds of gigabytes monthly, potentially triggering data cap penalties from ISPs that impose limits.
Technical Setup Requirements
While user-friendly once running, IPTV may require more technical setup than simply plugging a TV into a cable jack. You might need to configure set-top boxes, install apps on smart TVs, or use streaming devices. Though typically straightforward, this can be challenging for less tech-savvy users.
Service Reliability Variations
Quality varies significantly by provider. Well-established telecom IPTV services are often very reliable since they prioritize TV traffic on their managed networks. Smaller or newer IPTV providers might experience outages or inconsistencies, especially if their server capacity doesn’t match user demand.
Content Fragmentation
With IPTV and streaming, content rights are distributed across multiple providers. One service might not have every channel or show you want, potentially requiring multiple subscriptions. This fragmentation can be confusing and costly if not carefully managed.
IPTV Around the World: Global Perspective
IPTV has become a truly global phenomenon, with adoption patterns varying significantly by region.
Worldwide Adoption Scale
Over 300 million IPTV subscribers globally as of the mid-2020s demonstrates this isn’t a niche technology but a mainstream platform. The rapid growth reflects fundamental changes in how people prefer to consume television content.
Regional Leaders
Asia-Pacific dominates in user numbers, accounting for approximately 105 million users (≈42% of worldwide IPTV subscribers) in 2025. China is the single largest IPTV market, projected to reach 226 million IPTV subscribers by 2026 – over half the world’s total. This massive adoption is driven by government digitalization initiatives, expanding internet infrastructure, and bundled broadband packages.
Europe represents a mature IPTV market where telecom operators have successfully deployed comprehensive IPTV services. Countries like France, the UK, and Germany have significant IPTV penetration rates.
North America leads in IPTV revenue generation, accounting for over 40% of global IPTV market revenue, even though subscriber numbers are lower than Asia-Pacific. This reflects higher subscription prices and premium service tiers in American and Canadian markets.
The Global Cord-Cutting Movement
IPTV is central to the worldwide “cord-cutting” trend, where consumers abandon traditional cable and satellite subscriptions for internet-based alternatives. IPTV subscriber numbers will exceed cable TV subscribers by 2026, with IPTV adding approximately 63 million new subscribers between 2021 and 2026 to reach about 398 million users globally.
This dramatic shift represents more than just technology adoption – it’s a fundamental change in consumer expectations about television flexibility and control.
Content and Cultural Diversity
IPTV’s global reach enables unprecedented content diversity. Services cater to specific languages, cultures, and diaspora communities worldwide, allowing expatriates to access programming from their home countries. This global accessibility and niche content availability was difficult or impossible with traditional broadcast limitations.
Is IPTV Legal? Understanding Legitimate vs. Illegal IPTV
Given the proliferation of both legitimate and illicit IPTV services, understanding the legal landscape is crucial for consumers.
IPTV Technology is Completely Legal
IPTV as a technology is entirely legal – it’s simply a method of content delivery. Many legitimate broadcasters, telecommunications companies, and media organizations worldwide use IPTV to deliver licensed content to subscribers with proper authorization.
Legitimate IPTV Services
Legal IPTV services have proper licensing agreements with content creators, broadcasters, and studios. They pay for the rights to distribute copyrighted material, ensuring creators are compensated. These services might cost more to cover licensing fees but operate transparently and offer reliable customer support.
Examples include services from established telecommunications companies, recognized streaming platforms, and major media organizations.
The Future of IPTV
Multiple technological and market trends indicate IPTV will continue its rapid growth and further transform television consumption.
Continued Market Expansion
All indicators point to sustained IPTV growth. The global IPTV market is projected to grow at double-digit annual rates, with revenue forecasts suggesting the market could nearly double to $360+ billion by 2029. This growth is driven by expanding internet access worldwide – as more regions gain high-speed connectivity, IPTV becomes viable in more locations.
5G and Technology Advances
5G mobile networks will be transformative for IPTV, delivering high-bandwidth connections that enable seamless 4K and even 8K video streaming to mobile devices. This wireless capability will make IPTV truly accessible anywhere with 5G coverage, further expanding its reach beyond fixed-line connections.
Improved compression standards like HEVC/H.265 and upcoming codecs will make streaming more efficient, enabling higher quality video without massive data consumption.
Integration and Convergence
The distinction between IPTV and OTT streaming will continue blurring. Traditional IPTV providers are integrating popular streaming services into unified interfaces, while streaming platforms add live TV options. The future likely brings platforms that seamlessly aggregate content from various sources under single interfaces and billing systems.
Enhanced Personalization and Interactivity
Artificial Intelligence will drive unprecedented personalization, with IPTV services automatically curating channels and content based on individual viewing patterns. Interactive TV could expand dramatically, incorporating real-time features like sports betting, choose-your-own-adventure content, and deeper social media integration during live events.
Infrastructure and Policy Challenges
As IPTV grows, it must navigate challenges like net neutrality regulations, infrastructure capacity upgrades, and intensifying competition in crowded streaming markets. The ongoing fight against IPTV piracy will continue, likely with improved content protection and faster detection of illegal streams.
Conclusion
IPTV represents a fundamental shift in how television content is delivered and consumed. By delivering television through internet protocols rather than traditional broadcast methods, IPTV offers unprecedented flexibility, interactivity, and personalization that puts viewers in control of their entertainment experience.
With 250 million global subscribers and a market valued at $187 billion in 2025, IPTV has moved from experimental technology to mainstream entertainment platform. The dramatic growth trajectory – with projections suggesting IPTV will exceed cable TV subscribers by 2026 – demonstrates this isn’t a temporary trend but a permanent transformation of the television industry.
For consumers frustrated with expensive cable packages or rigid broadcast schedules, exploring legal IPTV options offers a path to more flexible, cost-effective television consumption. Whether through telecommunications providers offering comprehensive IPTV packages or streaming services providing live TV over the internet, the technology offers compelling alternatives to traditional television.
As internet connectivity continues improving worldwide and 5G networks expand, IPTV will become even more accessible and feature-rich. The era of Internet Protocol Television is truly just beginning, promising viewing experiences that are more personalized, interactive, and convenient than anything traditional broadcast television could offer. The future of television is increasingly internet-based, and IPTV sits at the center of this exciting evolution.




